

When and how was lithium discovered?Īround the 1800s, Brazilian chemist José Banifácio de Andrada discovered the mineral petalite in a mine in Sweden.
#Lithium atomic number portable#
Nearly all portable electronic devices, as well as power tools and electric automobiles, use these modern batteries. They are longer-lasting, faster charging, and more energy-dense than traditional batteries.

Lithium-ion batteries represent a revolution in electrochemistry. Each electrode can switch between acting as an anode or acting as a cathode, depending on the direction of the current flow through the cell. A carbon-based negative electrode and a metal-oxide-based positive electrode compose these batteries.
These batteries see their development in the early 1980s. The most prominent application of Lithium today is with electronics, specifically lithium-ion batteries. Another compound, lithium oxide, aids in the manufacturing of glass ceramics. Lighter vehicles can better maximize fuel efficiency. Since lithium is the least dense metal, it is very practical for creating lightweight vehicle components. Aluminum-lithium alloys find use in vehicle frames, such as in planes, trains, and automobiles.
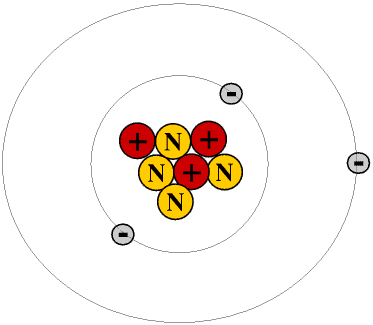
The most common alloy is the aluminum-lithium alloy, which has numerous industrial applications. Starting in 1949, salts such as lithium carbonate became an active ingredient in treatments for bipolar disorders as well as schizophrenia, with mixed results. Human nutrition does not require lithium as a trace mineral, but it has been used in various pharmaceutical applications over the last 70 years. A typical electron configuration for Li is 1s 22s 1. Its electronegativity reads as 0.98 on the Pauling scale. Like those sibling elements, Li has just one valence electron. It belongs to an elemental family known as alkali metals, which include sodium and potassium. Under hydrogen and after helium, Lithium, with the atomic symbol Li and an atomic number of 3, lies on group 1 of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
